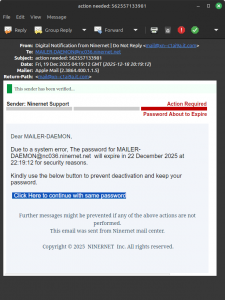
We just received a convincing phishing scam spam, which we’ve screenshotted here. (Click for a closer look.) You’ll note that we’ve become so famous that our name is even mentioned, although with the wrong capitalisation, of course. And, of course, there’s the usual copyright warning; we do not copyright server messages and any messages we send to you! What would be the point?!
Please note the following:
- The “from” address is not on the niner.net domain,
- The message was sent to an automated server address, and
- The link in the spam is to a site that includes “nc036.ninernet.net” in the URL, but this is not in the server part of the URL, it’s in the file name.
As we’ve said before, please treat every email you receive as spam or a scam — especially over the Christmas season — unless and until you can verify otherwise. (Don’t do the opposite, assume every message is real!) As far as legitimate mass messages from NinerNet are concerned, we post them here on our blog and usually (if not always) include a link in the email to our blog post. It’s that simple. If you’re not sure, simply ask us!